Inclusive Finance or Financial Inclusion means that everyone has access to affordable and useful financial services, such as savings, credit, insurance, loans, and equity. It also means that these services are delivered in a responsible and sustainable way. It is not possible without adequate financial literacy as it enables individuals to understand financial concepts and make responsible decisions that align with their financial goals and circumstances. Financial inclusion empowers economically disadvantaged and vulnerable segments of society to actively participate in national development by providing them with a safeguard against social and economic shocks.
Financial literacy is a *sine qua non for financial inclusion like an essential ingredient for a recipe or any essential action. Like yeast! It is a sine qua non for bread or wind, which is a sine qua non for flying a kite. Financial inclusion means that individuals and businesses have access to financial products and services that meet their needs, such as transactions, payments, savings, credit, and insurance. These services should be delivered in a responsible and sustainable way.
The World Bank Group (WBG) considers access to transaction accounts as a crucial step towards achieving financial inclusion. Transaction accounts enable individuals to store money and engage in payments, opening the door to other financial services. Despite progress made through the Universal Financial Access 2020 initiative, there is still considerable work ahead. To address this challenge effectively, measures such as establishing mobile banking services, collaborating with local financial institutions, and implementing educational campaigns on the benefits of transaction accounts should be prioritized.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released the National Strategy for Financial Inclusion 2019-2024 on January 10, 2020. It sets forth the vision and objectives of financial inclusion policies in India. The strategy was prepared by the RBI with inputs from the central government and financial sector regulators (Securities and Exchange Board of India, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India and Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority of India).
The report refers to financial inclusion as the process of ensuring access to financial services, and timely and adequate credit for vulnerable groups and low-income groups at an affordable cost. Financial inclusion has a multiplier effect in boosting overall economic output, reducing poverty and income inequality, and in promoting gender equality and women empowerment.
STEPS TAKEN FOR FINANCIAL INCLUSION:
Several steps have been taken by RBI to further financial inclusion in the country. These include:
(i) Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), under which 34 crore accounts have been opened with deposits amounting to Rs 89,257 crore (as of January 2019)
(ii) Schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana to provide accidental death or disability cover and Atal Pension Yojana to provide pension cover to subscribing bank account holders.
Furthermore, the bank-led model of financial inclusion adopted by the RBI through issuance of differentiated banking licenses (small finance banks and payments banks) and the launch of Indian Post Payments Bank in September 2018 has helped bridge the gap in last mile connectivity.
However, certain critical gaps remain an impediment for financial inclusion, such as:
(i) Inadequate infrastructure (in parts of rural hinterland, far flung areas in Himalayan and north-eastern region)
(ii) Poor tele and internet connectivity in rural hinterland, socio-cultural barriers.
(iii) Lack of market players in payment product space.
As per RBI the Financial Inclusion Index (FI-Index) has risen to 64.2 in March 2024, up from 60.1 in March 2023, indicating considerable progress in financial inclusion across the country.
The FI-Index is published annually in July every year.
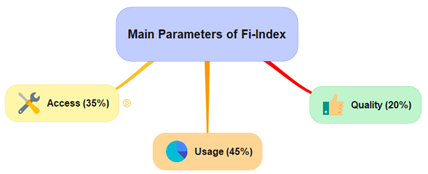
Source- IE
HOW TO ENABLE FINANCIAL INCLUSION AT GRASSROOT LEVEL
Financial inclusion can incorporate ease of access across a plethora of social constructs such as age, gender, race, region or socioeconomic standing. The parameters which can make transactions and investments more inclusive are as follows:
Affordable and Accessible Banking Services
By providing affordable and easily accessible banking services, we ensure that individuals who are unbanked or underbanked can actively engage in the formal financial system. Through the provision of no-frills savings accounts and low-cost transaction accounts, we enable financial inclusion right at the grassroots level. This, in turn, encourages people to save their money and establishes a sense of financial security, both in terms of conceptual peace of mind and physical protection.
Gender Inequalities
Statistics show that 31% of women are more prone to having inactive bank accounts compared to men. To address this disparity, tailored financial products, educational programs on financial literacy, and initiatives to support women's entrepreneurship are implemented. These efforts aim to provide women with the necessary tools and resources to actively participate in the formal financial system and achieve economic independence.
Consumer Protection
Financial inclusion involves protecting customers and implementing regulations to safeguard the interests of financially vulnerable individuals. Strong consumer protection frameworks ensure fair treatment, transparent pricing, and ethical conduct by financial institutions, fostering trust and confidence in formal financial services.
IMPORTANCE OF FINANCIAL INCLUSION
There are transparent and general reasons why financial inclusion is important. Some of the key reasons include:
- Financial inclusion reduces poverty and inequality.
- Financial inclusion promotes economic growth.
- Financial inclusion promotes small businesses.
- Financial inclusion empowers otherwise marginalized demographics
- Financial inclusion promotes innovation
- Financial inclusion may foster digital inclusion
FINANCIAL INCLUSION AND TECHNOLOGY
There are countless ways technology can and is playing a major role in enhancing financial inclusion. Here are some ways we can use modern innovations to better serve the world with financial services:
Mobile Banking
Mobile banking apps and online payment systems offer convenient and user-friendly ways to conduct financial transactions. Users can check account balances, transfer funds, pay bills, and even apply for loans. These services are available anytime, anywhere, eliminating the need to visit a physical bank branch. Online payment systems, like mobile wallets, store funds digitally and allow users to make payments using their mobile phones. Contactless payments with NFC technology and QR codes are also available for secure and swift transactions in retail settings, reducing the risk of theft or loss from carrying cash.
Online Lending Platforms
Fintech lending platforms facilitate direct connection between borrowers and lenders via online platforms. These platforms enable simplified lending procedure, granting individuals and businesses, often overlooked by traditional banks, access to credit that they would have otherwise been unable to secure.

ROLE OF GOVERNMENT IN PROMOTING FINANCIAL INCLUSION
Governments play a crucial and influential role in advancing financial inclusion through the implementation of policies and regulatory frameworks. They have the ability to enact initiatives aimed at diminishing obstacles, motivating financial institutions to cater to marginalized communities, and allocating resources towards promoting financial literacy programs and developing digital infrastructure.
Financial inclusion refers to the provision of accessible and affordable financial services that are responsible and tailored to meet the requirements of individuals and businesses. These services encompass various aspects such as payment facilities, savings options, credit opportunities, and insurance coverage.
TRANSFORMATIVE IN NATURE
Financial inclusion has the power to transform the lives of individuals and communities who have historically been excluded from formal financial services. By providing access to financial tools and resources, marginalized groups and MSEs can harness economic opportunities, build resilience, and improve their overall well-being. By prioritizing financial inclusion initiatives, we can create a more equitable and prosperous society for all. The impact and benefit of digital payment was clearly visible during the pandemic (covid) in recent years. It is an upward journey from here for sure!

FINANCIAL HEALTH AND FINANCIAL INCLUSION
When discussing financial well-being, it is common to confuse the concepts of financial health and financial inclusion. While they are related, they represent distinct aspects of an individual or a community's financial circumstances. While financial inclusion is an essential aspect of promoting financial health, it does not guarantee financial well-being. It is possible for individuals to have access to financial services but still struggle with poor financial management, high levels of debt, or inadequate savings. Conversely, individuals who may be financially healthy in terms of managing their finances may still face barriers to accessing traditional financial services due to their socio-economic circumstances
In other words, financial inclusion and financial health are strongly connected but are not synonymous. While financial inclusion focuses on providing access to affordable financial services, financial health encompasses the ability to meet financial needs, cope with unexpected expenses, and pursue financial goals. Additionally, the robust digital payments ecosystem in India, particularly the use of QR codes, has revolutionized the way people make everyday transactions, benefiting small street vendors and promoting economic growth.
CONCLUSION
Financial inclusion and digital payments play vital roles in driving economic development, empowering individuals, and fostering financial stability. It emphasizes the importance of providing affordable and appropriate financial services to underserved populations, such as low-income individuals, marginalized communities, and those living in rural areas. Financial inclusion aims to address barriers that prevent people from accessing financial institutions, such as limited physical access, lack of identification documents, or language barriers
*Sine qua non is a Latin phrase that means "without which not".
Disclaimer: The data and information has been sourced from various domains available to the public. We have taken utmost care to represent the same as factually as has been made available. Please do not make any decisions based on our blogpost. Kindly check the data & information independently. For further guidance on finance and investment please reach out to our experts at Investaffairs.
If you have any Personal Finance query, do write to us
Categories
Recent Posts






